WordPress is so popular software package for online publications, e-commerce, business sites, blogs, and all types of web sites that it has the major problem that comes with success: hackers. Sucuri, a business specialized in web site security, analyzed infected web sites that they had restored in 2018. WordPress was running on 90% of the infected sites.
Sucuri analyzed 18302 infected websites for the report where they summarize their findings. In 2018, web sites infected by malware or successfully accessed by hackers were powered by:
- 90% of the web sites were running on WordPress
- 4.6% Magento
- 4.3% Joomla
- 3.7% Drupal
Once infected, a web site is in trouble. Approximately 11% of the infected websites were marked dangerous by a blacklist authority whose listing is likely to affect negatively to Google search results.
It is fair to add that even though WordPress is the most hacked content management system, it is also – by a wide margin – the most popular system with millions of live installations.
The most common threats to WordPress and other content management systems
All content management systems, like WordPress have a similar problem that hackers are taking advantage of: third-party add-on modules, plugins, themes, and extensions are the most vulnerable element in a system.
It may take a long time before someone who has created a plugin is aware of a vulnerability, and before it is patched. Yet, open source content management systems want to provide add-on modules because they extend the functionality of the core system.
Common issues causing vulnerabilities:
- Improper deployment of the content management system.
- No security configuration.
- Overall site maintenance lacking knowledgeable resources.
- Broken authentication and session management.
- Pirated software with backdoors and other malware.
- Reuse of leaked passwords.
- Cross-site contamination.
By and large, plugins with known and unknown vulnerabilities are the primary attack route affecting tens of thousands of sites a year.
Three most desired files by hackers in WordPress
Index.php, functions.php and wp-config.php files are the most popular targets for attackers. These php scripts are loaded every time a site is accessed. They belong to a group of core files in WordPress.
The common types of infections in WordPress and other web sites
Sucuri detected the following type of hacks on infected WordPress sites:
- 68% of infected sites had a Backdoor. This is an access point to the system only known to the party who created the piece of software, such as a plugin.
- 56.4% Malware
- 51.3% SEO spam
- 44.4% Non-classified
- 18.9% Hack tool
- 12.5% Mailer
- 10.1% Defaced
- 8.9% Phishing
- 4.4% Dropper (a way to infect with a virus)
What can a WordPress site admin do to prevent hacking?
In 2018, 36.7% of infected sites had an outdated core WordPress version. It means the majority of hacked sites had an up-to-date WordPress configuration. Although constant updating of WordPress is encouraged, regular updating is clearly not the only protection method against hackers.
Multiple types of security and firewall plugins are available for making a WordPress site less vulnerable, as well as cloud services that monitor the health of a site.
The first step is to scan a WordPress site for known vulnerabilities. Free online scanners are available that can detect common problems and vulnerabilities hackers are looking for. Wpbeginner has reviewed a number of WordPress security scanning services. Many of these provide a subscription service that automates the scanning, and can conduct a deeper inspection inside the system.
We were worried about the status of WordPress security and privacy after December 2018 Wordcamp keynote speech State of the Word by Matt Mullenweg. He didn’t even mention security or privacy during his talk. If it is a sign of strategic direction for WordPress, it is a very risky one.
The news for the report via Info Security.

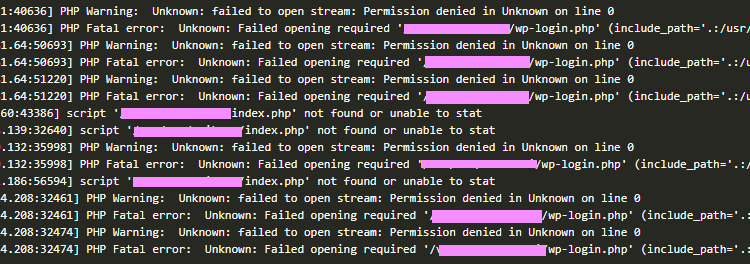

A major risk discovered for all WordPress sites that are using the Pipdig Power Pack (P3) plugin. My recommendation is to instantly remove it (no matter which version you happen to have). Delete all the files related to the plugin on your server.
WPTavern reports that the plugin has dangerous backdoors and has been used for attacks against other web sites. https://wptavern.com/pipdig-updates-p3-plugin-after-reports-expose-vendor-backdoors-built-in-kill-switch-and-malicious-ddos-code
Social Warfare, Yuzo Related Posts, Yellow Pencil Visual Theme Customizer WordPress plugins are being used for hacking sites and for attacking against other sites.
https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2019/04/a-security-researcher-with-a-grudge-is-dropping-web-0days-on-innocent-users/
These plugins have been removed from WordPress.org plugin database, but tens of thousands of sites are running them. Remove the plugin if your site has any of these.